Experimental validation of a computer-vision based method to assess the aerodynamic drag of cyclists
Keywords:
aerodynamics, 3D scanning, CFDAbstract
Reducing drag is a major challenge in cycling. In fact, it is a well-known fact that, on flat road conditions, aerodynamic drag represents about 80% of the total resistive forces applied to the cyclist. The aerodynamic drag is given by the following equation: 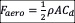 , where
, where  is the air density,
is the air density, 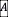 the cross-sectional area or frontal area and,
the cross-sectional area or frontal area and, 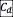 , the drag coefficient. In order to reduce the aerodynamic resistive forces, one search to minimize
, the drag coefficient. In order to reduce the aerodynamic resistive forces, one search to minimize 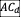 , which requires to be quantified. In the literature, different methods have been proposed; we can mainly quote: wind tunnel [1], dynamometric measurement [2], deceleration [3], linear regression [4], and 3D digitalization-based method [5-7].
, which requires to be quantified. In the literature, different methods have been proposed; we can mainly quote: wind tunnel [1], dynamometric measurement [2], deceleration [3], linear regression [4], and 3D digitalization-based method [5-7].
We previously introduced a new computer vision-based method to assess the aerodynamic drag of cyclists [8,9]: first a 3D+t model of the cyclist and his bike is built and thereafter this model is processed by a CFD solver to assess the aerodynamic resistive forces. This method offers a low cost alternative to the wind tunnel measurements and does not involve any special infrastructure (track) like the linear regression technique. Moreover, it overcomes the limitations of the classic «3D + CFD» methodologies that we investigated in a precedent work [8]. In previous work, we also evaluated performance of our method [9-10]. In this work we create a new dataset recorded in a wind tunnel and use it to experimentally validate our method.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2021 Journal of Science and Cycling

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors contributing to Journal of Science and Cycling agree to publish their articles under a Creative Commons CC BY-NC-ND license, allowing third parties to copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format, and to remix, transform, and build upon the material, for any purpose, even commercially, under the condition that appropriate credit is given, that a link to the license is provided, and that you indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
Authors retain copyright of their work, with first publication rights granted to Cycling Research Center.